7月1日,国际经典微生物学期刊Environmental Microbiology在线刊发题为“The cyclic lipopeptides suppress the motility of Vibrio alginolyticus via targeting the Na+-driven flagellar motor component MotX”的文章,报道了中国科学院海洋研究所孙超岷研究组关于深海细菌环脂肽类抗生素抑制病原菌运动新机制的研究成果,为发展新型深海微生物源抗生素提供了新的靶点和理论依据。
在前期研究中,孙超岷研究组在分离深海微生物的过程中偶然发现一株芽孢杆菌能有效抑制水产重要病原溶藻弧菌的运动,而运动能力很大程度上影响着病原菌的致病性。基于这一发现,研究人员借助生物化学手段分离并解析了抑制病原菌运动的活性物质的结构(Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017),明确了该活性物质为一种新型环脂肽类抗生素,但对其抑制病原菌运动的具体机制并不清晰。本研究中,研究人员进一步利用转录组学和分子遗传学等手段,精确定位了该环脂肽类抗生素的作用靶点为病原菌鞭毛分子马达的关键组分MotX,解释了该抗生素为何能有效抑制病原菌的运动和致病性。更为重要的是,MotX在各种能侵染水产动物和人类的病原弧菌(包括鳗弧菌、灿烂弧菌、副溶血弧菌和创伤弧菌等)中广泛存在,该环脂肽类抗生物素对上述各类病原弧菌的运动也具有显著的抑制效果,而不抑制缺乏MotX细菌的运动能力,是一种极具应用潜力、广谱且有选择性的抗菌药物,相应细菌菌株和化合物的产权和相关信息已经申请国家发明专利保护。
实验海洋生物学重点实验室刘瑞副研究员为第一作者,孙超岷研究员为通讯作者。本研究得到了国家重点研发计划、大洋协会“深海生物资源计划”及中科院战略先导专项等项目联合资助。
近年来,孙超岷研究组围绕深海细菌脂肽类抗生素进行了系统研究,分别解析了丰原素(Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018)、表面活性素(Marine Drugs, 2019)和伊枯菌素(Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2020, 修稿中)等脂肽分子的结构和作用机制,为脂肽类抗生素的进一步开发应用奠定了坚实基础。
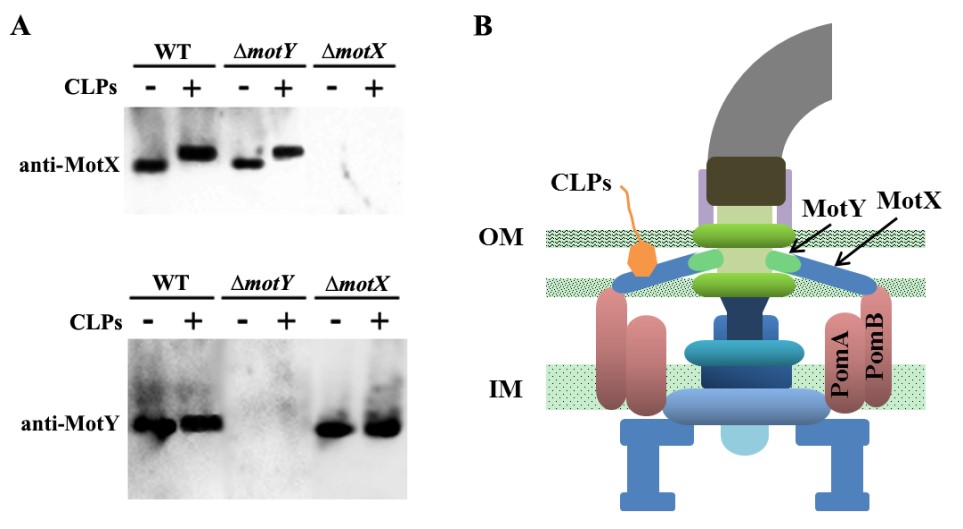
环脂肽类抗生素作用于溶藻弧菌鞭毛分子马达关键组分MotX
论文DOI: 10.1111/1462-2920.15144;
论文链接:https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15144
本文涉及的研究论文:
1. Rui Liu, Rikuan Zheng, Ge Liu, Chaomin Sun*. The cyclic lipopeptides suppress the motility of Vibrio alginolyticus via targeting the Na+-driven flagellar motor component MotX. Environmental Microbiology. 2020. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.15144.
2. Shengnan Zhou, Ge Liu, Rikuan Zheng, Chaomin Sun* and Shimei Wu. Structural and functional insights of iturin W, a novel lipopeptide produced by the deep-sea bacterium Bacillus sp. wsm-1. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2020, in revised.
3. Shimei Wu, Ge Liu, Shengnan Zhou, Zhenxia Sha, Chaomin Sun*. Characterization of antifungal lipopeptide biosurfactants produced by marine bacterium Bacillus sp. CS30. Marine Drugs, 2019, 17, 199; doi:10.3390/md17040199.
4. Linlin Zhang, Chaomin Sun*. Fengycins, cyclic lipopeptides from marine Bacillus subtilisstrains, kill the plant-pathogenic fungus Magnaporthe grisea by inducing reactive oxygen species production and chromatin condensation. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2018, 84(18).
5. Pengyuan Xiu, Rui Liu, Dechao Zhang*, Chaomin Sun*. Pumilacidin-like lipopeptides derived from marine bacterium Bacillus sp. suppress the motility of Vibrio alginolyticus. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2017, 83(12). doi: 10.1128/AEM.00450-17.